Table of Contents
Industrial pumps are indispensable for mobilizing many types of machinery in manufacturing and in the industries of wastewater, oil & gas, and chemical processing. For OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), pumps are not just components, they are lifelines that ensure machines continue to run under pressure.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide the information to help you know about the different types of industrial pumps, how to choose the right one, sourcing, and how they are being considered in OEM systems for high performance and reliability.
What Are Industrial Pumps?
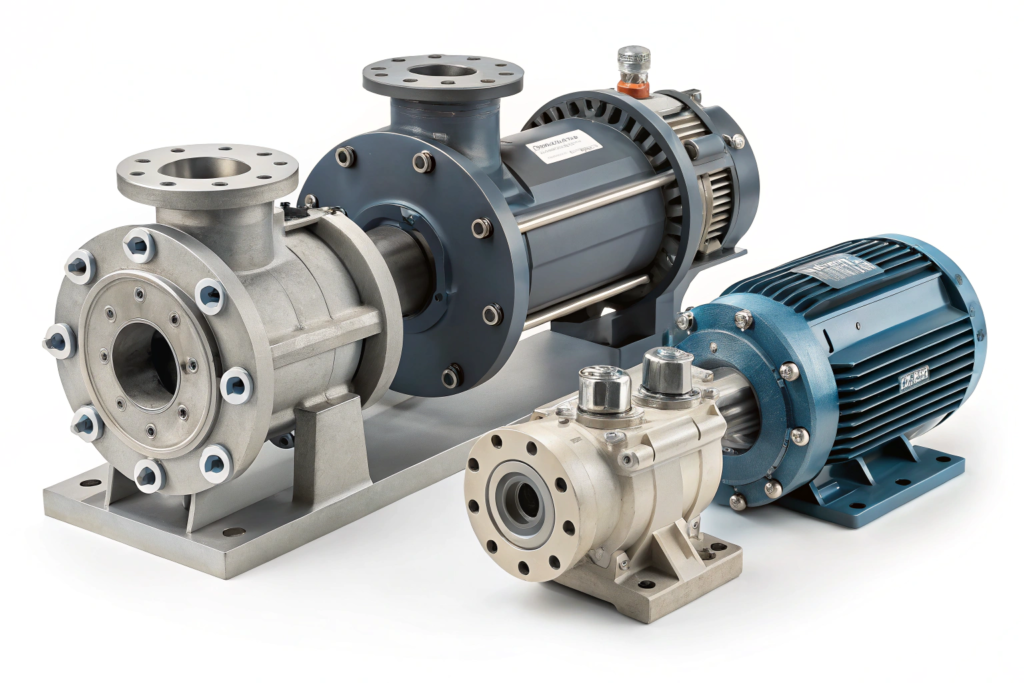

Industrial pumps are mechanical devices designed to transport fluids (liquids, gases, or slurries) from one location to another. Industrial pumps typically differ from domestic pumps in that they are designed to handle high flow, high pressure, corrosive materials, and are intended for continuous service rather than intermittent use.
Some of the main components of an industrial pump include:
- Impeller. Drives the fluid via rotation.
- Pump Casing. Houses the internal components of a pump and controls the fluid path.
- Motor/Driver. Powers the pump.
- Seals and Bearings. Provide pressure containment and reduce friction.
Types of Industrial Pumps
1. Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of industrial pump. They move fluid with a rotating impeller by converting kinetic energy to pressure.
- Water supply
- Cooling systems
- Chemical processing
- Irrigation
Advantages: Simple design, inexpensive, appropriate for low-viscosity fluids.
2. Positive Displacement Pumps
These operate by moving fluid by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe.
- Reciprocating Pumps
Includes piston, diaphragm, and plunger pumps. Use Cases: High pressure applications where fluids are metered, oil, & gas.
- Rotary Pumps
Includes gear, screw, and vane pumps. Use Cases: Viscous fluids including oils, syrups, and greases
3. Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are intended to pump fluid while submerged. The motor is sealed to protect it from water damage.
Best For:
- Sewage treatment
- Drainage
- Mining & construction site pumping applications.
A common application of a submersible pump is a sewage pit. Using submersible pumps is beneficial in OEM applications where space is limited or it is important to pump fluid many feet into the ground.
4. Specialty & Custom Pumps
Some pumps that do not fit into the categories above include; pumps rated for higher pressures (high-pressure), magnetic drive pumps, multi-stage pumps etc. These pumps are special or custom in nature to suit unique requirements for some OEM or industrial application.
Best For:
- Handling hazardous chemicals
- Pumping water from greater depths (deep wells)
- Handling fluids precisely, and controlling fluids exactly in OEM machines that are customized and unique.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Pump

Key Selection Factors
- Flow Rate (Q): Fluid quantity needed over period of time
- Total Head: The vertical lift the pump must perform
- Fluid Characteristics: Viscosity, corrosiveness, temperature
- System Pressure: The inlet and outlet pressures required
- Environment: Outdoors, dust, corrosive or cleanroom
Mistakes to Avoid
- Undersizing: Can result in overheating or overloading your pump
- Oversizing: Wastes energy and increases costs
- Ignoring Materials Compatibility: Wrong choice of materials can lead to corrosion or pump failure
- Ignoring Maintenance Space: Poor layout could make later servicing a challenge
Industrial Pump Supply & Sourcing
Where to Buy Pumps
- Directly from the Manufacturer: Best for custom or bulk orders
- Authorized Distributor: Best for quick, small orders
- OEM-Approved Partners: Provide design integration and engineering support
Checklist for Supplier Evaluation
- Established/Validated track record in your industry
- ISO or appropriate certification
- Ability to supply spare parts
- Technical support & documentation
- Post sales service and Annual Maintenance Contract options
Pumps for OEM Applications
- Each machine may restrict flow, pressures or space or be different altogether
- Long-term dependability for brand image
- Consistency when producing in large volumes depends on stable suppliers
Triple D’s OEM Pump Solutions
- Select the best pump for your application
- Make change to the casing or dimensions to fit layout
- Confirm operation is in accordance with industrial specs
- Scale to align your production quantity or goals
Maintenance & Troubleshooting Basics
- Typical Maintenance Tasks
- Listen for strange noises or vibrations
- Watch seals and gaskets for leakage
- Check lubrication level in bearings
- Clean filters and strainers regularly
Frequent Complications
- Cavitation: Related to pressure or air in the system
- Seal Failure: Related to wear or chemicals
- Overheating: Related to running dry or being overloaded
- Flow Drop: Related to filters in contact with debris or an impeller hitting something
Trends in Industrial Pump Technology
- Intelligent Pumps
- Industrial pumps are now IoT-enabled and can stream data related to pressure, flow, and temperature in real-time
- Great for predictive maintenance and remote monitoring
- Energy-Efficient Models
- Use optimized impeller geometries, and variable-speed drives to minimize power consumption
- Helpful for OEMs that want to comply with green standards
- Advanced Materials
- We can now use alternative materials that are corrosion resistant alloys and non-metallics (e.g. PTFE)
- Increases life in demanding chemical or high-temperature areas, etc.
Industries That Depend on Industrial Pumps
- Oil & Gas: Drilling, fluid transfer, refinery
- Chemical & Pharma: Handling aggressive chemicals, sterile solutions
- Water Treatment: Pumps for sewage, desalination, recycling
- Food Processing: Hygienic pumps for milk, juices, syrups
- Textile: Cooling systems, dye solution circulation
- OEM Machinery: Custom machines in every sector with fluid transfer.
Conclusion
Industrial pumps are more than just parts; they’re performance drivers. Selecting the proper pump can impact energy consumption, machine life and replicability for original equipment manufacturers manufacturing progressively larger systems.
With extensive engineering experience and robust end-to-end support, Triple D We Make Motors enables the reliability and customization that today’s industries depend on.